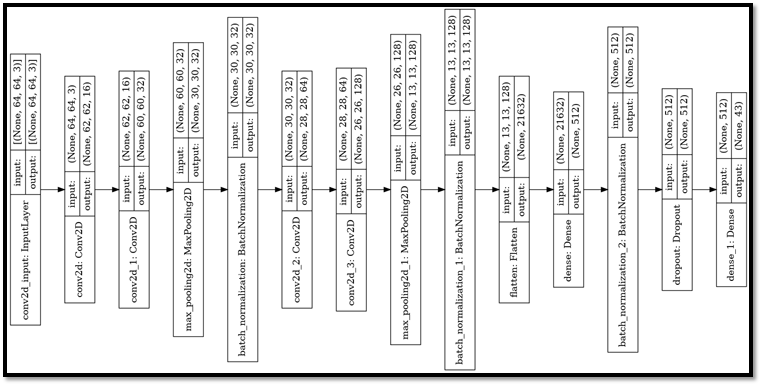
NO AUGMENTATION
Description:
The model architecture with different convent layers followed by fully connected layers is as shown below. Computed accuracy with just Pre-processing and fit the training data to the model.
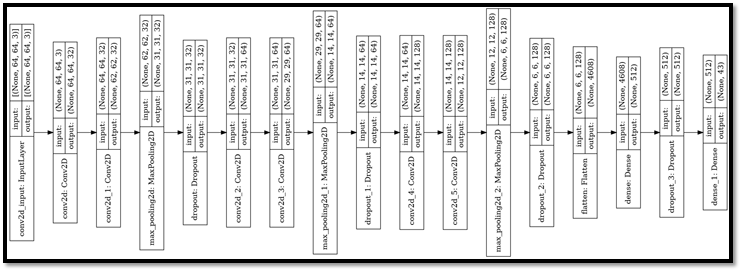
DATA AUGMENTATION
Description:
In image data augmentation, we take a single image from the available images, apply some transformation techniques like right shift, left shift, and zooming. Transformed versions of images in the training dataset that belong to the same class as the original image are created in this process. The transformation should be chosen carefully otherwise the dataset may become out of the contest.

ALEXNET
Description:
AlexNet is one of the most popular neural network architectures to date. It was proposed by Alex Krizhevsky for the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRV), and is based on convolutional neural networks. ILSVRV evaluates algorithms for Object Detection and Image Classification. In 2012, Alex Krizhevsky et al. published ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. This is when AlexNet was first heard of.
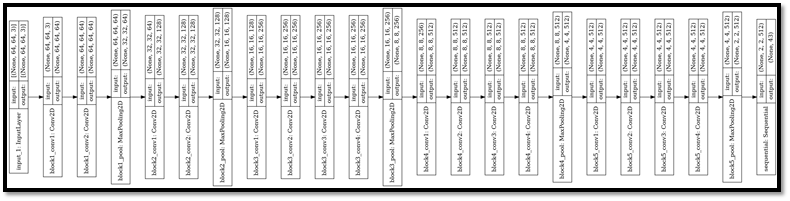
VGG-19
Description:
VGG-19 is a trained Convolutional Neural Network, from Visual Geometry Group, Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford. The number 19 stands for the number of layers with trainable weights. 16 Convolutional layers and 3 Fully Connected layers.
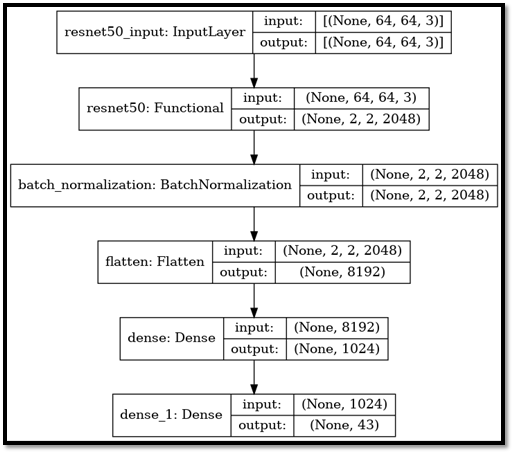
RESNET50
Description:
one of the bottlenecks of VGG is that they couldn’t go as deep as wanted, because they started to lose generalization capability. ResNets solve’s this known as vanishing gradient. This is because when the network is too deep, the gradients from where the loss function is calculated easily shrink to zero after several applications of the chain rule. This result on the weights never updating its values and therefore, no learning is being performed. With ResNets, the gradients can flow directly through the skip connections ackwards from later layers to initial filters.